More sensitive macro factors
advertisement

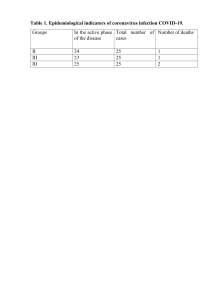
Assessment of default probability in conditions of cyclicality Totmyanina Ksenia Moscow, 2014 Actuality • Corporate sector represents a significant part of banking business worldwide. • Loans to corporates are a significant part of Russian banking portfolio: to the end of 2013 loans to corporates reached 56% of total credit portfolio and 39% of total assets of Russian banks. • Number of researches devoted to corporate credit risk estimation is strongly limited, especially for emerging market economies. • Level of non-performing loans in corporate portfolio is increasing this fact can lead to instability of Russian financial and banking system • Construction companies are the most widespread among Russian borrowers and at the same time very exposed to systematic risks Object of research – Russian contracting companies Item of research – Assessment of default probability Purpose of research The purpose of our research is to develop an empirical model for estimation default probability of potential corporate clients of Russian banks. The key steps to achieve this purpose are: • research the different approaches to default definitions • represent the classification of existing models to default modeling, review the advantages and disadvantages of these models • analyze the nature and sources of the procyclicality effect, represent the review of available instruments to mitigation of the procyclicality effect • collect the sample of financial indicators for defaulted and non-defaulted companies and macro factors for the specified period • execute a statistical analysis to determine the sensetive financial indicators and macro factors • execute a multivariable analysis to build sets of logit models • analyze the quality and predictive power of final model and represent the economic interpretation of the observed relationship Default definitions There are a lot of approaches: • Default as non-fulfillment the conditions of the loan agreement due to inability or unwillingness of the borrower • Default as the bankruptcy • Default based on BIS criteria: overdue more than 90 days and / or bank considers that the debtor is unable to repay the loan Review of default models Probability of default models 1.2 Market-based models Structural models 1.1 Fundamental-based models 1.1.1 Models based on financial statements Reduced forms Scoring models 1.3 Advanced models Linear discrimination models Fuzzy sets models Multiple discrimination Neuron networks Univariate discrimination Binary choice models 1.1.3 Rating-based models 1.1. 2 Macroeconomics models Cohort approach Exogenous factors Duration approach Endogenous factors Procyclicality issue Procyclical effect - increased business cycle fluctuations Sources can be different: 1) Prudential control: for example, capital adequacy requirements increase during periods of recession and reduce during the period of growth 2 ) The behavior of economic agents: for example, lending activity increase in periods of growth and decrease in periods of recession 3) Expectations of economic agents: for example, the risk is underestimated in the periods of growth, and overestimated during recessions 4) The corporate governance system: for example, the KPI systems and bonuses for managers Mitigations of procyclicality Procyclicality mitigation instruments via inputs data EAD conversion TTC LGD via outputs data Other parameters Time horizon Quantile TTC PD Conter-cyclicality index Capital buffers Dynamic provisions Scalar factor Stress-testing Macro factors Financial parameters that can be statistically significant Group of financial factors potentially affecting the level of credit risk: • Size • Profitability • Turnover • Financial stability We formed a long list of financial indicators from each class above - finally total list consists of 31 indicators Sample for modeling • All defaulted companies in constructing industries during 2005-2013 – 159 companies • Default = bankruptcy • For each defaulted companies we had 3 analogical (same size and industry) non-defaulted companies – 477 non-defaulted companies Defaults dynamics 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 Univariate analysis: selection of the risk dominant financial indicators Instruments: 1) Analysis and normalization of data (Chebyshev’s inequality) 2) Statistical tests to identify the most descriptive variables (Student's test, Welch tests, ANOVA test) More risk-dominant factors: Balance value Return on sales Working capital Share of stocks in current assets Return on assets Profitability of expenses Coefficient of autonomy Univariate analysis: selection of the risk sensitive macro indicators Instruments: 1) Analysis and normalization of data (Chebyshev’s inequality) 2) Regression models between macro factors and average default rate (based on S&P data) More sensitive macro factors: Oil price Export of goods and services Imports of goods and services Current account Unemployment rate Loans to individuals Multivariate analysis: a binary choice model Binary logit-models: where if the company is default otherwise set of financial and macro factors Multivariate analysis On the basis of selected financial indicators and macro variables, all possible multivariate models were built The resulting combination was selected based on following criteria: • No significant correlation • Significance of indicators (t-statistic and F-test) • The highest value Mc Fadden R2 Multivariate analysis: results Best model (Mc Fadden R2=32%): • Stocks in current assets, profitability of expenses, coefficient of autonomy and import are most risk sensitive • Share of stocks in current assets was included in the quadratic form that led to increase of R2 by 2% Quality of model – classification table Model results Observed Classification table Non default Default Non default 84% (TN) 53% (FP) Default 16% (FN) 47% (TP) • Model better predicts no default cases • With the exclusion of macroeconomic indicators the quality of the model decreases Thank you for your attention!