lab4.
advertisement
Фильтрация прослушиваемых пакетов (Capture Filters) в Ethereal
Использование фильтров
Фильтры сбора позволяют собирать не всю информацию из разделяемой сетевой среды, а лишь кадры
необходимые для анализа возникшей проблемы, поэтому нужно провести предварительный анализ
решаемой задачи для выявления признаков проблемных кадров.
Наряду с фильтрацией можно использовать ограничение собираемых данных по длине (truncate - усечение).
Имейте в виду, что сбор большого количества кадров или сбор больших кадров увеличивает время
обработки кадров и увеличивает размер буфера для собранных пакетов. Это может вызвать потерю пакетов,
поэтому вы должны ограничивать длину усечения до минимально возможного значения достаточного чтобы
захватить информацию требуемых вам протоколов.
Встроенное значение составляет 68 байтов, этого достаточно для IP, ICMP, TCP и UDP но может исключить
информацию протоколов DNS и NFS.
Создание фильтров
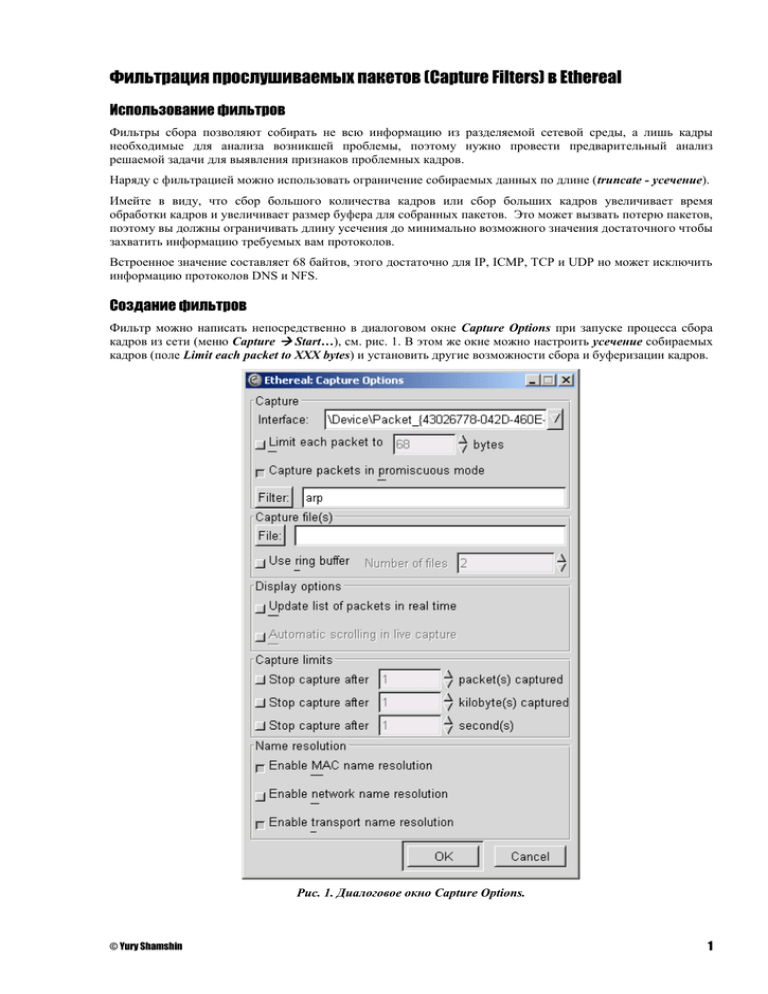
Фильтр можно написать непосредственно в диалоговом окне Capture Options при запуске процесса сбора
кадров из сети (меню Capture Start…), см. рис. 1. В этом же окне можно настроить усечение собираемых
кадров (поле Limit each packet to XXX bytes) и установить другие возможности сбора и буферизации кадров.
Рис. 1. Диалоговое окно Capture Options.
© Yury Shamshin
1
Другой вариант создания фильтров сбора – использование диалогового окна манипуляции фильтрами, см.
рис. 2. Для вызова используйте меню Edit Capture Filter либо кнопку Filter в окне Capture Options.
Рис. 2 Диалоговое окно Capture Filter
Окно Capture Filter позволяет:
создать новый фильтр: написать Filter name, Filter string и нажать New;
изменить имеющийся фильтр: выбрать фильтр – отредактировать – Change;
создать копию имеющегося фильтра: выбрать фильтр – Copy – отредактировать – Change;
удалить имеющийся фильтр: выбрать фильтр – Delete;
сохранить изменения для последующих сеансов: Save.
Если фильтр будет содержать синтаксические ошибки, то parser (синтаксический анализатор) программы
Ethereal сгенерирует соответствующее сообщение.
Например, при попытке активировать фильтр, содержащий имя, которое невозможно разрешить в IP или
MAC адреса, “arp src or dst ws-303” будет выдано предупреждающее сообщение (см. рис. 3) и сбор пакетов
прекратится.
Рис. 3. Предупреждение о синтаксической ошибке в фильтре.
Другой пример некорректного фильтра “(arp or ip) src or dst mail.parks.lv”, следует использовать “arp src or
dst mail.parks.lv or ip src or dst mail.parks.lv”
© Yury Shamshin
2
Синтаксис фильтров сбора
Фильтр сбора (capture filter) представляет из себя логическое варажение задаваемое при запуске процесса
сбора кадров из сетевой среды (Ethernet). Если фильтр не задан, то собираются все пакеты. Если фильтр
задан, то будут собраны лишь пакеты для которых выражение является истинным. В Ethereal используются
соглашения о формате задания фильтров соответствующие программе tcpdump.
В соответствии с этими соглашениями, выражение (expression) состоит из одного или более примитивов
(primitives). Примитивы обычно состоят из идентификатора id (имя или число) следующего за одним или
более классификаторами (qualifiers).
Выделяются следующие три типа классификаторов: type, dir, proto.
type – классификаторы типа
Определяют к какому типу имеет отношение идущий за ними id.
Возможными типами являются host, net и port.
Если классификатора типа не задан, то считается что это host.
Например, “host foo”, “net 128.3”, “port 20”.
dir – классификаторы направлений (от directions)
Определяют конкретное направление передачи в id и/или из id.
Возможными направлениями являются src, dst, src or dst и src and dst.
Для point to point протоколов связи (например, slip), чтобы указать желаемое направление могут
использоваться классификаторы inbound (приходящие) и outbound (уходящие).
Если классификатор напрвления не задан, то считается что это src or dst.
Например, “src foo”, “dst net 128.3”, “src or dst port ftp-data”.
proto – классификаторы протоколов (от protocols)
Ограничивают сравнение с конкретным протоколом.
Возможные значения протоколов: ether, fddi, tr, ip, ip6, arp, rarp, decnet, tcp и udp.
Если классификатор протокола не задан, то подразумеваются все перечисленные протоколы.
Например, “ether src foo”, “arp net 128.3”, “tcp port 21”.
Документация по фильтрам сбора
Ethereal uses the libpcap filter language for capture filters. This is explained in the tcpdump man page. If you can
understand it, you are a better man that I am, Gunga Din!
You enter the capture filter into the Filter field of the Ethereal Capture Preferences dialog box, as shown in Figure 39. The following is an outline of the syntax of the tcpdump capture filter language.
A capture filter takes the form of a series of primitive expressions connected by conjuctions
(and/or) and optionally preceeded by not:
[not] primitive [and|or [not] primitive ...]
An example is shown in Example 3-2.
Example 3-2. A capture filter for telnet than captures traffic to and from a particular
host
tcp port 23 and host 10.0.0.5
This example captures telnet traffic to and from the host 10.0.0.5, and shows how to
use two primitives and the and conjunction. Another example is shown in Example
3-3, and shows how to capture all telnet traffic except that from 10.0.0.5.
Example 3-3. Capturing all telnet traffic not from 10.0.0.5
tcp port 23 and not host 10.0.0.5
A primitive is simply one of the following:
57
Chapter 3. Using Ethereal
[src|dst] host <host>
This primitive allows you to filter on a host IP address or name. You can optionally
© Yury Shamshin
3
preceed the primitive with the keyword src|dst to specify that you are
only interested in source or destination addresses. If these are not present, packets
where the specified address appears as either the source or the destination
address will be selected.
ether [src|dst] host <ehost>
This primitive allows you to filter on Ethernet host addresses. You can optionally
includethe keyword src|dst between the keywords ether and host to specify
that you are only interested in source or destination addresses. If these are
not present, packets where the specified address appears in either the source or
destination address will be selected.
gateway host <host>
This primitive allows you to filter on packets that used host as a gateway. That
is, where the Ethernet source or destination was host but neither the source nor
destination IP address was host.
[src|dst] net <net> [{mask <mask>}|{len <len>}]
This primitive allows you to filter on network numbers. You can optionally preceed
this primitive with the keyword src|dst to specify that you are only interested
in a source or destination network. If neither of these are present, packets
will be selected that have the specified network in either the source or destination
address. In addition, you can specify either the netmask or the CIDR prefix
for the network if they are different from your own.
[tcp|udp] [src|dst] port <port>
This primitive allows you to filter on TCP and UDP port numbers. You can optionally
preceed this primitive with the keywords src|dst and tcp|udp which
allow you to specify that you are only interested in source or destination ports
and TCP or UDP packets respectively. The keywords tcp|udp must appear before
src|dst.
If these are not specified, packets will be selected for both the TCP and UDP protocols
and when the specified address appears in either the source or destination
port field.
less|greater <length>
This primitive allows you to filter on packets whose length was less than or
equal to the specified length, or greater than or equal to the specified length,
respectively.
ip|ether proto <protocol>
This primitive allows you to filter on the specified protocol at either the Ethernet
layer or the IP layer.
58
Chapter 3. Using Ethereal
ether|ip broadcast|multicast
This primitive allows you to filter on either Ethernet or IP broadcasts or multicasts.
<expr> relop <expr>
This primitive allows you to create complex filter expressions that select bytes or
ranges of bytes in packets. Please see the tcpdump man pages for more details.
© Yury Shamshin
4
